What are SVI settings? On the Switch, SVI determines the logical layer-3 interface. It is a routed interface that shows the IP addressing space for a specific VLAN. In a local area network, VLANs work to separate the broadcast domain. When the Host wants to communicate with another host in a different VLAN, the traffic needs to be routed in VLAN.
In this article, we’ll explain SVI, like what are SVI settings? How do you configure SVI? Its benefits, characteristics, and FAQs. Without further ado, let’s get to the topic!
Table of Contents
What do you know about SVI?
SVI stands for switched Virtual interface, which is the logical layer-3 interface. An inter-VLAN routing was accomplished due to SVI. Inter-VLAN is when the Host in one virtual LAN wants to connect with another host on a different Virtual LAN; then the traffic is routed among them.
Switched VI is a virtual interface that connects the VLAN on a device with a layer 3 router engine in the same device. Just one VLAN juncture can connect with VLAN, but before that, you need to do a configuration on VLAN juncture for VLAN. The process happens only if you want to route between VLANs or to give IP hosting to the device via virtual routing and VRF (virtual forwarding). When you allow VLAN juncture establishment, the switch will generate the VLAN juncture for default VLAN, allowing remote configuration for switches.
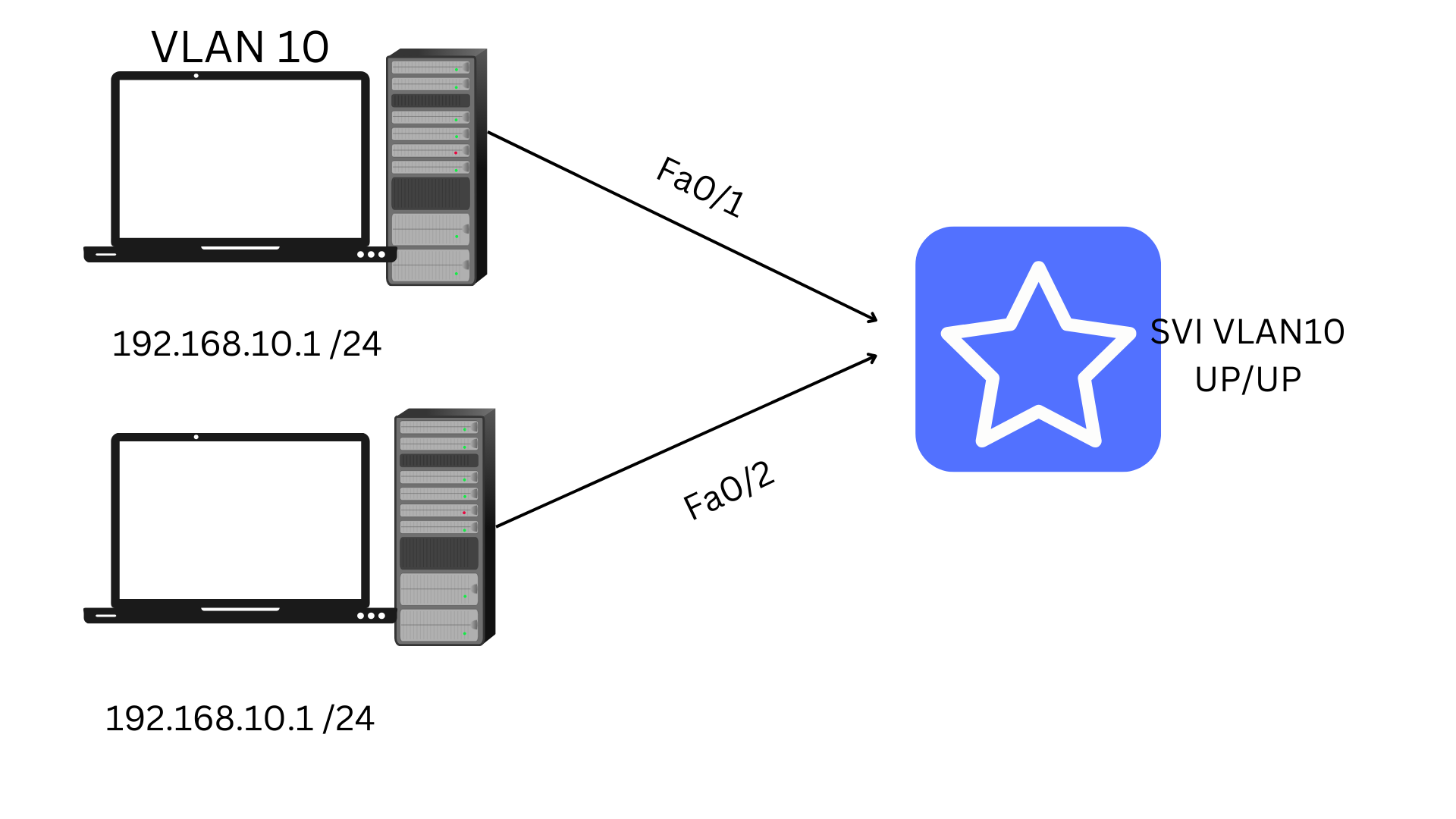
However, SVI is a port that only conveys untagged-VLAN data frames for managed switches. Within VLAN and SVI, one-to-one mapping occurs, and just one SVI settings can be mapped to VLAN.SVI is only activated when it is linked with any physical port. SVI is also referring as a routed VLAN interface for some of the vendors.
SVI was created as a security protocol and works for Switch ports protection. It does not link with the physical interface on the switch. The interface also allows the connection of multiple types of media. Devices that want the connection from a remote place using SVI.
SVI settings act as a logical interface rather than a physical one and are linked with one VLAN. Meanwhile, While the routed port is a physical port that works as one of the router ports. The port assists with all routing protocols. Just it does not assist the VLAN sub-interface and has no links with any VLAN.
uses
The switched virtual interface is on the layer 3 interfaces of the switches that work by routing to another VLAN (broadcast domain). In the process default gateway act as the Internet protocol for SVI. It is used in Cisco ACI Fabric as if switched VI the router a destination MAC address, then it will route the data packets.
Characteristics
The characteristics of the Switched virtual interface are in the following section:
- It does not have a connection with any physical interface.
- It allows handling switches from any location.
- By default, SVI connects with VLAN1.
Advantages of SVI settings:
The advantages of the SVI are in the below section:
- SVI is fast compared to the router on a stick because it is hardware-switched and routed.
- It takes lesser time as in routing there is no need for external links from the switch to the router.
- Throughput is greater as layer 2 EtherChannel is present between switches and provides large bandwidth.
SVI settings configuration
SVI settings are designed for Default VLAN to allow remote switching. A switch does not work or activate until it connects to a physical port. The multilayer switch offer configuration of VLAN as a logical interface for routing. The configuration refers to VLAN number are:
Switch(config)#interface VLAN 10
Switch(config)# description TEST
Switch(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shut
For inter-VLAN routing, SVI is the general method. To work online Logical VLAN must fulfill the following needs:
- Creation of VLAN.
- One of the VLAN ports must be active.
Reason for SVI settings configuration for VLAN:
Switched virtual interfaces configuration on VLAN for some reasons such as:
- It allows the network traffic to be routed in VLANs and offers a default gateway for it.
- SVI offers bridging if it is essential like non-routable protocol.
- Offers layer 3 Internet protocol connection to switch.
- Assist with bridging and routing protocol.
Let’s take another example: we create two SVI on layer 3 VLAN 10 and 20. The switch must, as Layer 3, is one important thing to get the desired result. The basics for switch configuration are the hostname, global configuration mode, interface configuration, and IP address assigning.
VLAN 10
SWITCH (config)#vlan 10 create Layer 2 for VLAN 10
SWITCH (config)#interface VLAN 10 generates the SVI for VLAN 10
(config-if) #description WORKSTATIONS
SWITCH (config-if) #ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 assign IP address
First, create layer 2 for VLAN 10. The following line determines to generate SVI for VLAN 10 of layer 3. The following line is unnecessary; it just wants you to add an interface description that helps you know the purpose of SVI. The end step is to allocate the IP to a created SVI for VLAN 10. The example generates two SVIs for the workstation and server VLANs.
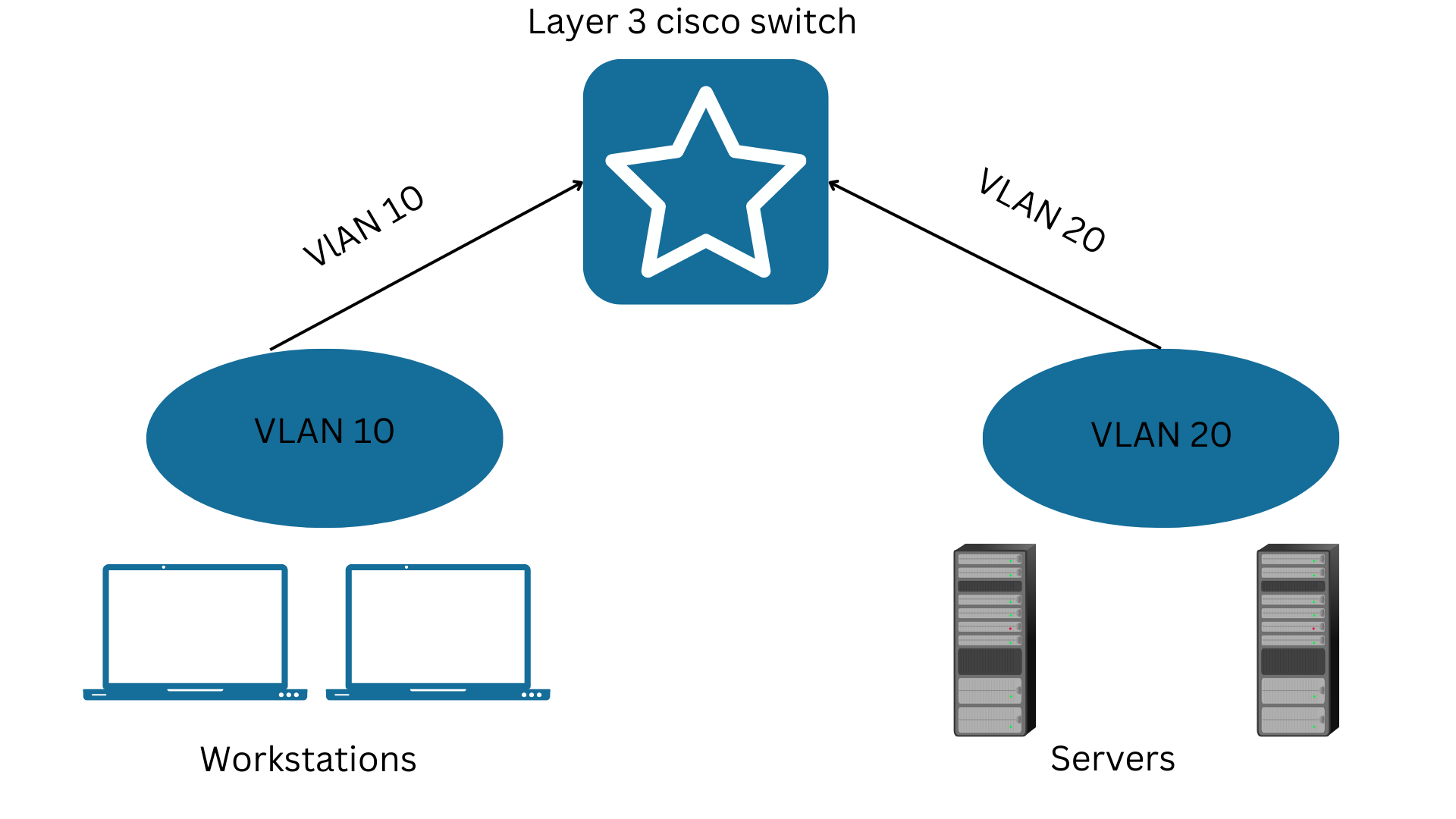
The commands for the SVI configuration of VLAN 20 are the following:
SWITCH (config)#vlan 20 <– create Layer 2 VLAN 20
SWITCH (config)#interface VLAN 20 <- now create the SVI for VLAN 20
SWITCH (config-if) #description SERVERS
SWITCH (config-if) #ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 <- assign IP address to SVI
The process to delete the Switched virtual interface are:
- In the interface option, choose the interface to delete.
- Tap on remove SVI.
- A dialogue box asks you to confirm if you want to delete the SVI.
- Tick on copy running configuration to startup configuration check box to copy the SVI configuration on startup-config.
- Tap on submit.
Frequently asked questions
Q: What is the reason for using SVI on Cisco switch?
Ans: Switched virtual interface shows the logical rather than the physical interface among VLAN Bridging and routing functions on a device. SVI contains physical ports, direct port channels, or virtual ports.
Q: Do you know about Default SVI on Cisco switch?
Ans: SVI is virtual, and VLAN 1 is the interface that is, by default, enabled on the Cisco switch.
Q: Are SVI and VLAN are same?
Ans: VLAN (virtual local area network) is the broadcast integrated and isolated on the OSI model’s data link layer (2 layers). The switched virtual interface does not have a virtual port but works the same as the VLAN router interface. SVI is also referring as Interface LAN.
Q: How to find the SVI IP address?
Ans: When the enable command executes, then the show running-configuration command or the show IP interfaces brief command provides the IP address of SVI to users.
Q: How do you convert SVI to a layer 3 switch?
Ans: The steps to convert SVI to layer 3 switch are the following:
- At first, generate two VLANs.
- Now create an SVI VLAN interface and then configure it for each VLAN.
- Determine the ports that provide access.
- Enable the IP address.
Final words
SVI is a logical (virtual) interface whose work is to transfer the VLAN frames that do not have an address in a switch. A one-to-one mapping exists in VLAN and SVI. The configuration of SVI is simple to create layer 2 and then SVI VLAN, identify the access port and enable the IP address. We have also discussed the configuration with examples in the article above. To get a proper understanding, read it from the start!

Leave a comment