In telecommunication, a duplex system is an end-to-end system that comprises two or more two or more two connected devices or parties that can communicate with each other in both directions (bidirectional). Well, there are three modes of transmission. One is simplex, other two are half duplex and full duplex. The mode of transmission tells about the direction of signal flow among two connected devices or parties. Connected devices in a duplex communication system are present in an Ethernet environment.
The duplex communication system is in works in many communication networks. Either it allows simultaneous communication in both directions between connected devices or it provides a reverse way for monitoring and remote adjustment in the field.
Table of Contents
The key difference between the three transmission modes:
The main difference between the three transmission modes is that,
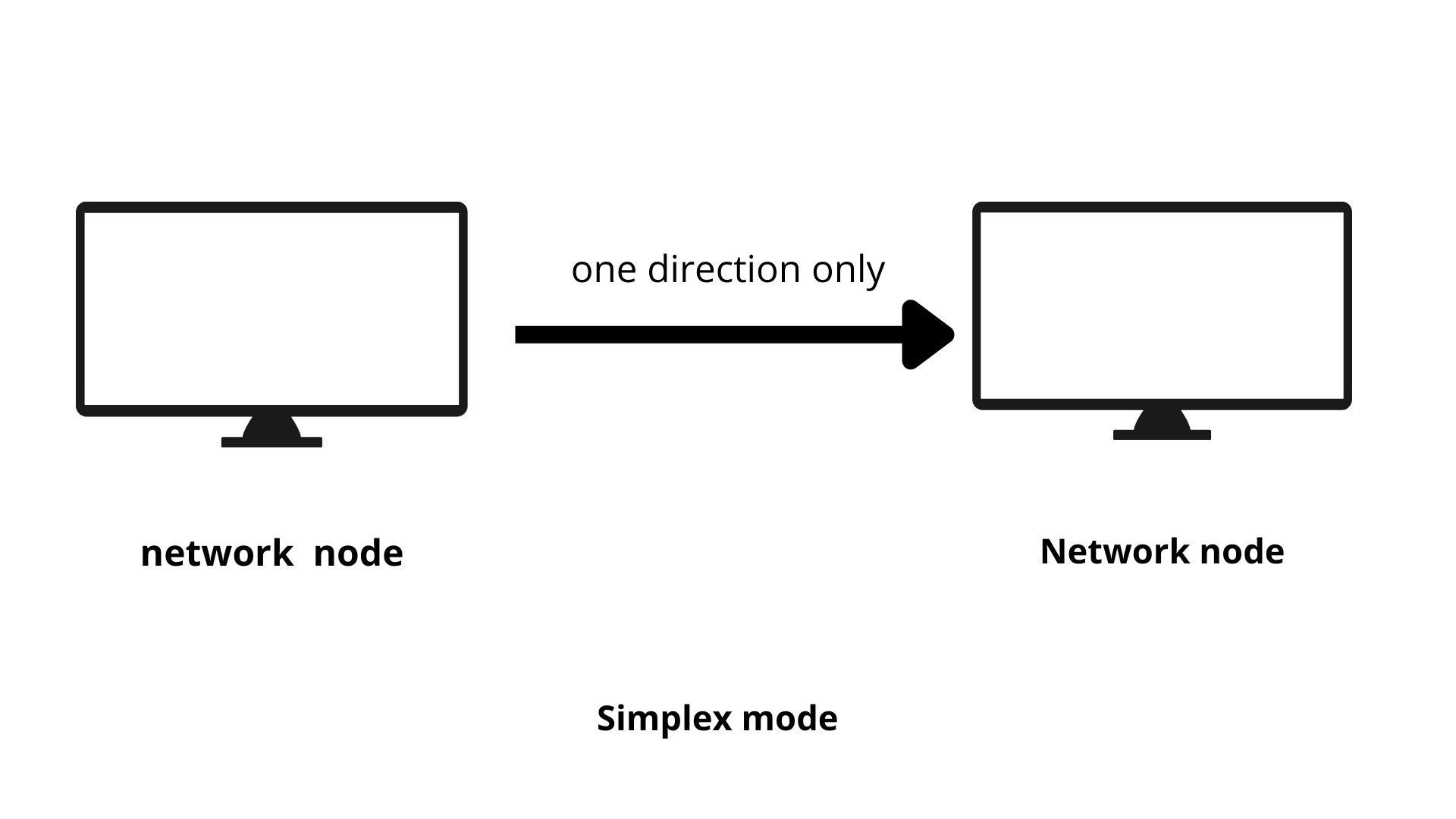
- In simplex transmission mode, the communication path is unidirectional or irreversible.
- In the full-duplex mode of transmission, the communication path is bidirectional. Channel is in work by both of the connected parties at the same time.
- While in the half-duplex mode of transmission the communication path is bidirectional or two ways but the channel is in work replaceable by both of the connected parties.
- In half-duplex, both parties communicate signals but not at the same time. While in full duplex both devices transmit signals simultaneously.
- Transmission in simplex only one device communicates signal. E.g., the keyboard sends the signal to the monitor but the monitor does not respond to the monitor.
- Telephone communication is in work by full-duplex where both connected parties communicate with each other.
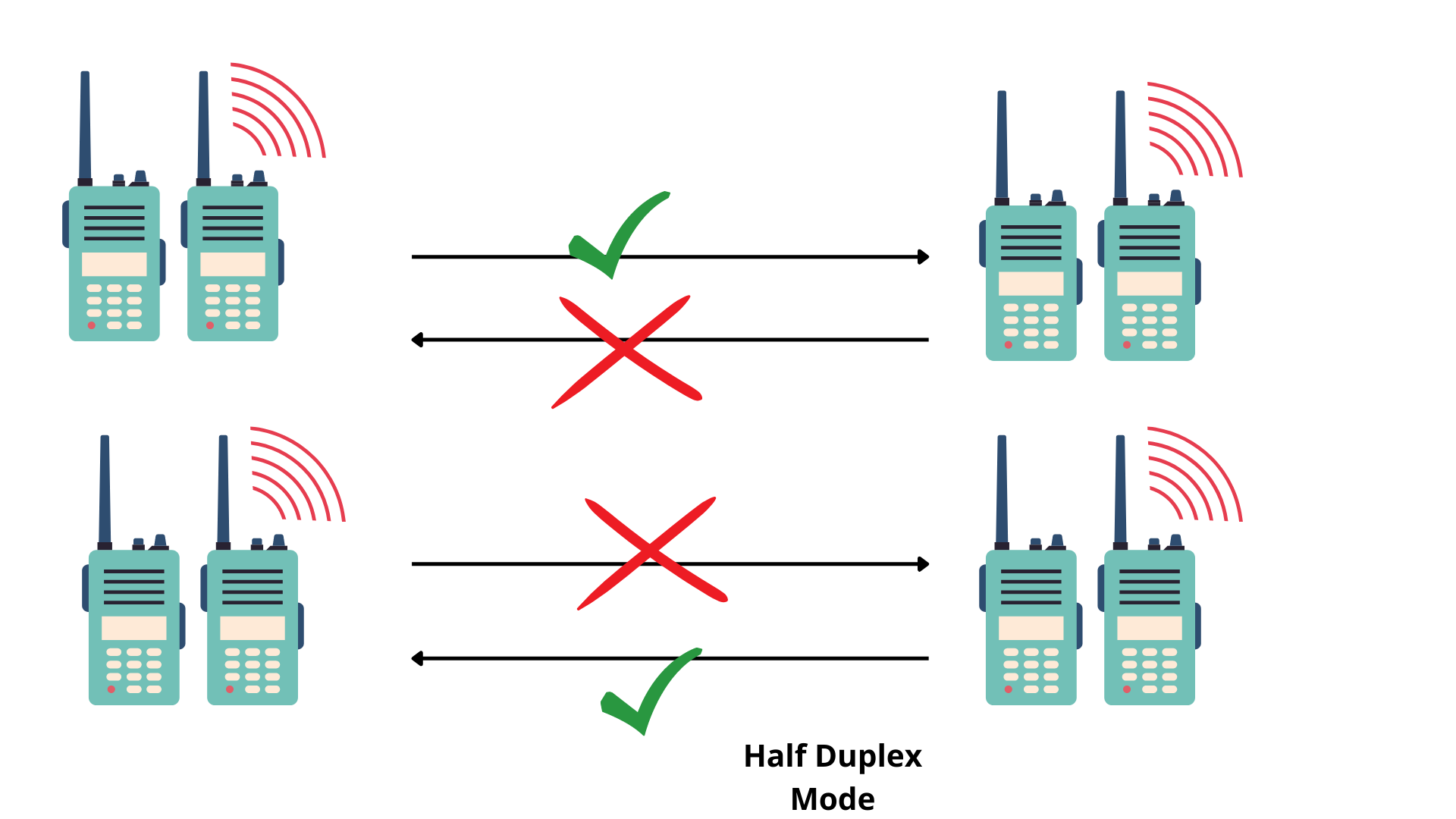
- Using a walkie-talkie in a half-duplex in which both connected parties communicate but not at the same time. They have to take turns.
- In all three modes of transmission full duplex transmission offers the best performance. It also maximizes the amount of bandwidth.
In other words, the primary difference between these two duplexes is in the full duplex system can send and receive data at the same time while half-duplex communication work in one direction simultaneously. Let’s dig more to explore the comparison between half duplex and full duplex.
What is a Half duplex?
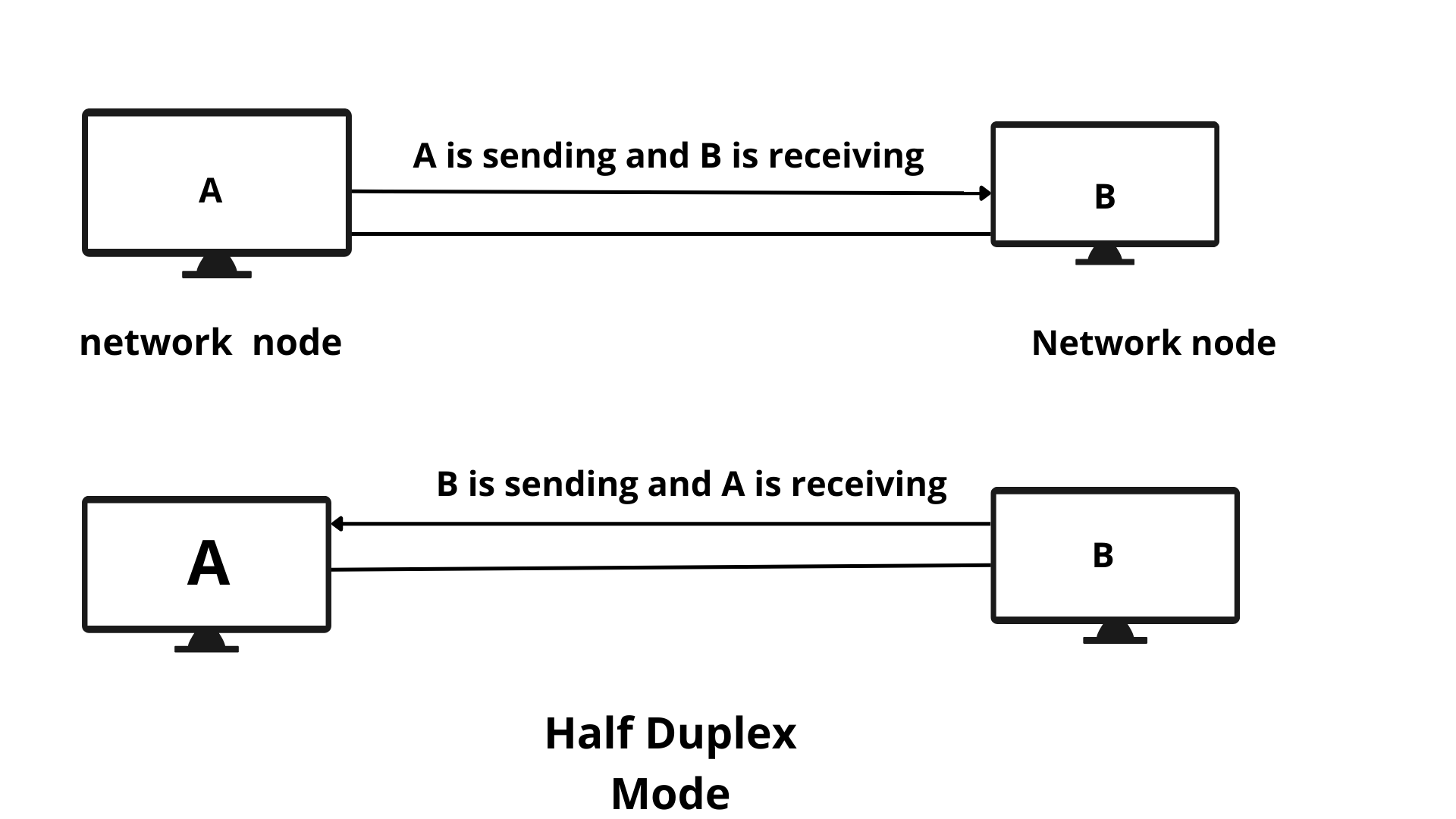
In telecommunication, half duplex is described in such a way that the communication between the sender and receiver takes place in both directions but one at a time. Both sender and receiver are allowed to send and receive information but at a time only one is allowed to do that. Still half duplex is considered a one-way road in which vehicles traveling in the opposite direction have to wait until the road is empty for crossing.
Channel on a half-duplex only one thing present on that channel is a node. This node can talk or transfer data one at a time. In which when one data completes its task then another node starts transmitting data. If various nodes try to transfer information at the same time, then a collision occurs on the network, and as a consequence data loss or error might happen.
Half duplex requires a mechanism or process to avoid these collisions in the network. The work method is known as carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD). Firstly, Ethernet devices that are using the half-duplex mode first reckon to see if anything is in a way of transferring before they attempt to send. If something is sent it will have to wait before trying again.
For example, in a walkie-talkie (DECT phone, TDD 4G, or 5G phones) both speakers can speak one at a time. In a walkie-talkie, one must use the word over or any other decided keyword that indicates the end of transmission. It ensures that only one device is transmitting at a time. Half duplex communication system conserves the bandwidth at the expense of reducing the overall output. Only one communication channel is shared between two directions. Walkie-talkie also uses a single frequency for both directions. In contrast cell, phones or telephones used two frequencies to carry the signals in each direction.
What is a full duplex?

In full duplex transmission mode, both sender and receiver communicate with each other simultaneously. They can send and receive data at the same time. A full duplex is like a two-way road there is no need to wait before transmitting. It can flow in both directional, or bidirectional. In which two nodes are responsible for sending and receiving data simultaneously.
Full duplex there are no chances of collisions or data loss. In any communication, data are transferred very quickly. For example, telephone communication. Since they allow both callers to communicate and be heard simultaneously. It is accomplished on a two-wire circuit via the use of a hybrid coil in a telephone hybrid. Modern cell phones are also operated via full duplex.
There is some distinction between full-duplex communication, it uses the same physical communication channel for both directions. From the user point of view technical distinction does not matter and both the devices are referred to as full duplexes. Ethernet connections achieve a full duplex by using two pairs of twisted pairs in the same jacket. In which one pair is for sending while the other pair is for receiving.
It has many advantages on half duplex. Because there is only one transmitter on each pair of wires so there are no chances of Collison’s and no time is wasted in retransmit frames. In both directions, full transmission capacity is present because their receiving and sending functions are separate.
Comparison chart:
| Base of comparison | Half duplex | Full duplex |
| Communication direction | Bi-directional but one at a time | Two ways directional but simultaneously communicate |
| Rate of performance | Better than simplex transmission | The best mode of transmission |
| Sending and receiving | It can send and receive one at a time | Full duplex sends and receives simultaneously |
| example | Wookie talkie | Communication through telephones |
On a shared medium like coaxial cable in which several nodes are attached to it. All nodes share the channel because they check if the channel is free before transmitting. When more nodes share the channel, lower will be the effective output of each node. The main reason is waiting is increased access.
When two nodes are talking on separate sub-channels or in full duplex mode via Cat 5 cable. E.g., when separate pairs of wires communicate, they carry data in each direction. When more than one pair of wires are trying to communicate full-duplex have a hard time separating the data sent through the various nodes. It will enhance the cost and decrease efficiency. While in media shared in the half-duplex by more than two nodes but full duplex does not communicate more than pair of nodes.
Up-to-date Ethernet standards such as 10G and above are working out the demands to support the half-duplex modes.
Difference between half duplex and full duplex transmission modes:
| Serial no. | Base of comparison | Half duplex | Full duplex |
| 1. | Definition | The sender can send and receive data but one task at a time. | In full duplex mode, the sender can send and receive data at the same time. |
| 2. | Channel handling | Half-duplex uses one channel. | While transmitting full-duplex use two channels because the channel needs to split for separate sending and receiving. |
| 3. | Performance | Less performance than a full duplex. | It provides better performance than a half-duplex. |
| 4. | Flow of data | Two directional but one at a time | The flow of data is two-way and simultaneously. |
| 5. | Communication channel | Half-duplex conserves the bandwidth as it is exchanged on both sides on a single communication channel. | Entire bandwidth is used in splitting the communication channel so that transmission is possible in both directions at the same time. |
| 6. | Bandwidth | less bandwidth used. | The utilization of bandwidth is doubled that of a half-duplex. |
| 7. | Preferable for | It is preferable when data send in both directions but in the opposite way. | Suitable for communication in both directions simultaneously without time wasting. |
| 8. | Transmission | In half-duplex two devices are connected end to end for transmitting and receiving. Both transmit signals but one at a time. | A signal is transmitted in both directions. Both end stations can send and receive. Two independent channels are required for transmission. One for data sending and the other for receiving. |
| 9. | Examples | Text messages and DECT phones. | Cell phones, telephones audio video calls, and instant chat rooms. |
More Examples:
 Especially, Ethernet hubs are half-duplex devices as they have a single channel of communication. On the other hand, Ethernet switches use both communications. WI-FI networks are also a half-duplex based on a channel. WIFI 6 standards use multiple communication channels simultaneously. It creates the potential for full-duplex communication.
Especially, Ethernet hubs are half-duplex devices as they have a single channel of communication. On the other hand, Ethernet switches use both communications. WI-FI networks are also a half-duplex based on a channel. WIFI 6 standards use multiple communication channels simultaneously. It creates the potential for full-duplex communication.

[…] needs to be established. It is additive into two categories. One is a full duplex and the other a half-duplex. A half duplex is for one channel while a full duplex is specific for two channels. The limitation […]
[…] router works in the full-duplex transmission mode. However, we can change it manually to work on half duplex […]
[…] receiver. It is two wired protocols. Rx and Tx signal lines are used by data cables. It works on a full duplex mode which means sending and receiving at the same time to different boards. Data are transmitted and […]