In computer networking, a wireless bridging helps to join two networks so that the network communicates with each other. It serves as a single network. With the advancement in technologies, WIFI and other wireless networks are increasing in popularity, and the need to connect these networks and with the older wired networks are also expanded. Through bridge internetwork connections are possible. This connection consists of network protocol as well as hardware.
Table of Contents
Wireless bridge:
The simple definition of wireless bridging is that it is the type of networking device that allows the over-the-air connection between two different segments of a LAN (Local area network). Microwaves and radio signals or laser spectrum are used by the wireless bridging to provide fixed wireless access.
A wireless bridge is also referred to as a WI-FI bridge, it works like a wired network bridge. The bridge plays a very important role in LAN segments. These segments are located or separated in different physical locations. The system has an antenna to send and receive the radio signal. The antenna can connect to a wired LAN switch or router. It is a perfect alternative when,
- If the wired LAN connections are costly.
- A wired link cannot work for logical or technical reasons.
Types of wireless bridging:
The hardware that supports network bridging are these,
-
Wi-Fi to WIFI bridge:
Wi-Fi to Wi-Fi bridge supports two Wi-Fi networks. It increases the coverage area of the Wi-Fi hotspot. Bridging in Ethernet as well as in WI-FI mode is supported by wireless AP hardware.
-
Wi-Fi to Ethernet bridge:
This bridge connects Wi-Fi clients to an Ethernet network. The hardware interacts with WIFI wireless access points. It is often most useful for older computers or devices that do not have WIFI accessibility.
-
Bluetooth to WIFI bridge:
This hardware supports connecting devices that communicate with Bluetooth gadgets and interface with a Wi-Fi home network.
Example:
Wireless bridging is commonly in use to accommodate many buildings in one company. Legal wireless bridging between two buildings is accommodating with an extension. Wireless mesh is a service that enables a wireless access point to connect via radio. Bridging enable the use of wireless mesh. The most common example of wireless bridging is that provides connectivity between two buildings by using the outdoor wireless link as shown in the figure.
A wireless bridge uses two access points in a transport layer 2 bridge. So, between the access points as long as a clear RF line and the distance between the access points is within the range of access points, the bridge can connect to another building.
Why do we use wireless bridging?
Wireless bridging is mostly used to connect two buildings with outdoor access points. In the figure, the network is located in building A. so instead of using cables between two buildings which are more expensive use two outdoor access points that have been configured for the wireless mesh. These access points of building B are connected with the network in building A. that is why the access points on the building must be dual radio network portals.
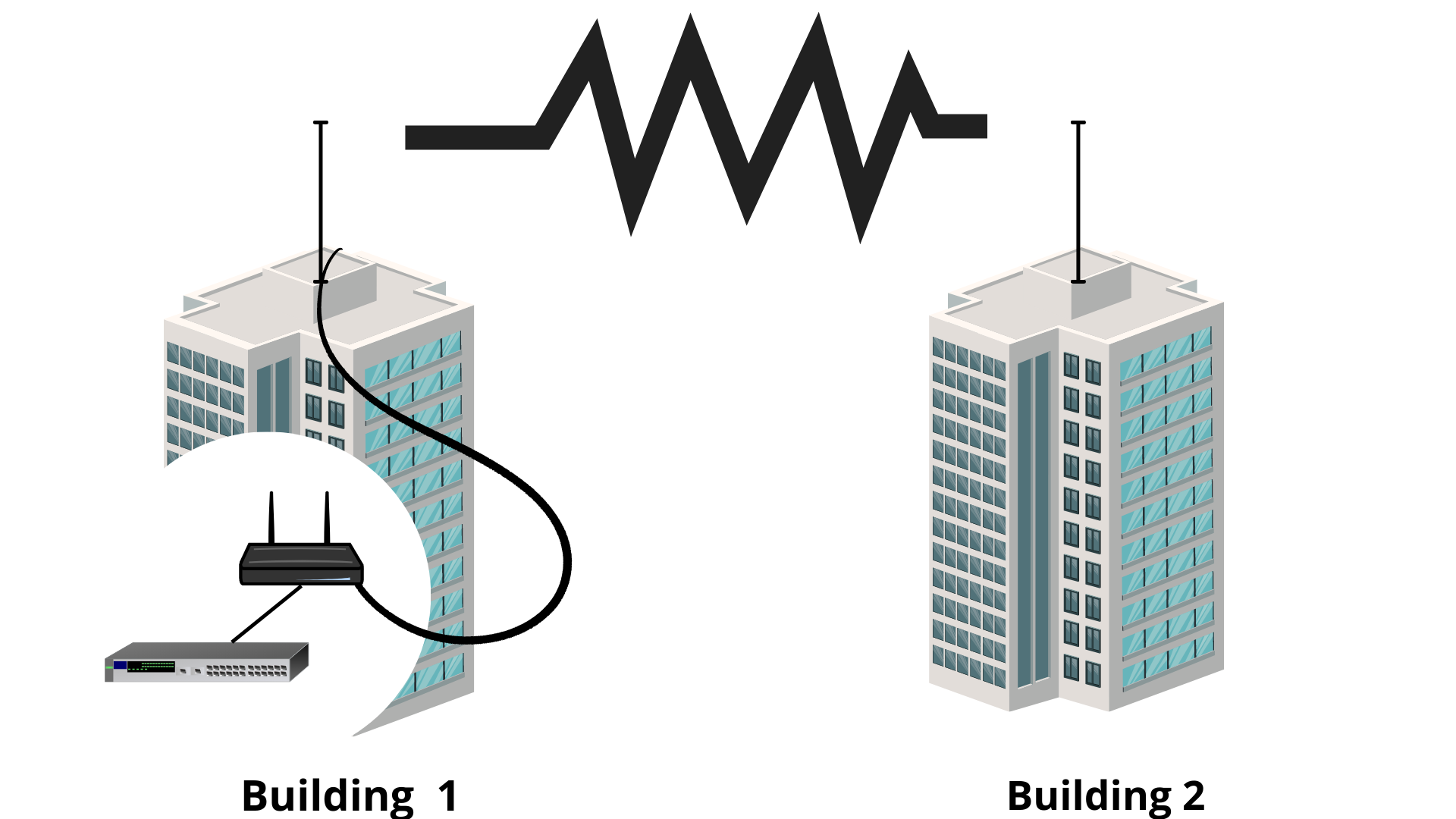
Working of wireless bridging:
Wireless bridging has a special network called the wireless mesh network. It is linked between the wired mesh protocol and associated mesh access points as shown in fig. The wireless bridge also has the two-mesh protocol. In this case, both outdoor access points must have a dual radio point, with one of their radio access points configured with a WLAN service protocol.
When a wireless bridge operating, a mesh access point serves as the bridge picks up the packets from the wired and transfers them to other bridge points. A simple destination learning mechanism is to prevent forwarding unnecessary packets across the bridge.
Configuration of wireless bridging:
If you want to configure a wireless bridge must do the following to create it,
- Firstly, configure a mesh SSID make sure to enable bridging when you authorize Mesh on the setting tab.
- Second, connect access points to a controller and allow them to work as the access points of wireless bridging.
- Disconnect the connection between access points from the controller and then keep them in the bridge layout.
There are two major classes of wireless bridging,
- Microwave and radio wave bridges use the radio signal in the 2.4 to 80 GHz range for transferring data.
- FSO (free space optics) laser links, which use an optical signal for data transfer. The optical signal is usually from outside the visible spectrum.
There is an Ultra-narrowband filter – a precision optical filter, Ultra-narrowband filters are ideal for use as laser line, laser cleanup, or laser excitation filters in applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, and DNA sequencing.
Free space optics:
Laser or optical offer a good speed and interference-free wireless bridge. The limitation is that fog and the sun sometimes block the light that connects both ends. A laser link will not go down from 1Gbps to 100Mbps in the event something like this causes interference in the line-of-sight path. It will stop working until the hindrance is clear. This cause problem for a business that needs constant uptime to work efficiently.
Radiofrequency or microwave bridge:
RF and MV bridges operate in a wide range of frequencies. The most common are,
- 4 GHz: it is used for short links and provides a speed of less than 300Mbps.
- 3GHz: wireless ISPs are used this and require a license. It provides a low connection to users.
- 5GHz: license can be exempted for (A and B) or licensed for (B and C). Used for links of < 300Mbps.
- 6-38GHz: It is licensed to provide speed up t 1Gbps over long distances. When this operating in the UK needs to be careful because not all of this spectrum is usable.
- 60GHZ: usable for links speed up to 1Gbps over distance range is 800m to 1600m.
- 70GHz: licensed is light and usable for links up to 1Gbps.
- 80GHz: light licensed and usable of 1Gbps over a very long distance than 60 and 70GHz.

The above mention frequencies require the line of sight for work in their full capacity. Based on the nature of radio frequency there is an area of wireless propagation b/w the known link as the Fresnel zone.
Frequently asked the question:
Q no 1: Can the wireless bridge have an access point?
Ans: if the two endpoints you have you need a bridge, if you have more than 2 then you need a wireless access point.
Q no 2: How wireless bridge works?
Ans: wireless bridge use end-to-end technology to connect two endpoints wirelessly. So, by using frequency radio waves, a wireless bridge can transfer up to 20Gpbs.

Leave a comment